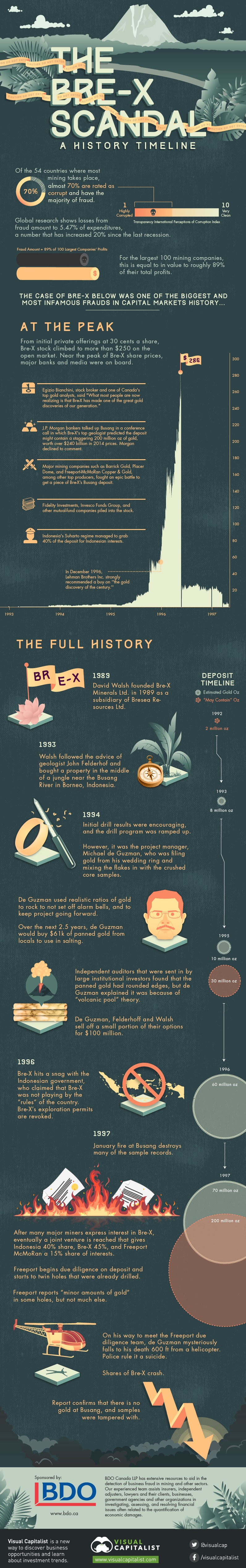
Bre-X Scandal: A History Timeline
Sponsored by: BDO and BDO Natural Resources LinkedIn Group This infographic documents the rise and fall of Bre-X. From initial private offerings at 30 cents a share, Bre-X stock climbed to more than $250 on the open market. Near the peak of Bre-X share prices, major banks and media were on board: The Peak
It was touted by media and banks as the “richest gold deposit ever” In December 1996, Lehman Brothers Inc. strongly recommended a buy on “the gold discovery of the century.” Major mining companies such as Barrick Gold, Placer Dome, and Freeport-McMoRan Copper & Gold, among other top producers, fought an epic battle to get a piece of Bre-X’s Busang deposit. Indonesia’s Suharto regime managed to grab 40% of the deposit for Indonesian interests. Fidelity Investments, Invesco Funds Group, and other mutual-fund companies piled into the stock. J.P. Morgan bankers talked up Busang in a conference call in which Bre-X’s top geologist predicted the deposit might contain a staggering 200 million oz of gold, worth over $240 billion in 2014 prices. Morgan declined to comment. Egizio Bianchini, stock broker and one of Canada’s top gold analysts, said “What most people are now realizing is that Bre-X has made one of the great gold discoveries of our generation.”
The Timeline:
1989: David Walsh founded Bre-X Minerals Ltd. in 1989 as a subsidiary of Bresea Resources Ltd.
1993: Walsh followed the advice of geologist John Felderhof and bought a property in the middle of a jungle near the Busang River in Borneo, Indonesia.
1994: Initial drill results were encouraging, and the drill program was ramped up.
1994: However, it was the project manager, Michael de Guzman, who was filing gold from his wedding ring and mixing the flakes in with the crushed core samples.
De Guzman used realistic ratios of gold to rock to not set off alarm bells, and to keep project going forward. Over the next 2.5 years, de Guzman would buy $61k of panned gold from locals to use in salting.
Independent auditors that were sent in by large institutional investors found that the panned gold had rounded edges, but de Guzman explained it was because of “volcanic pool” theory.
De Guzman, Felderhoff and Walsh sell off a small portion of their options for $100 million
1996: Bre-X hits a snag with the Indonesian government, who claimed that Bre-X was not playing by the “rules” of the country. Bre-X’s exploration permits are revoked.
1997: January fire at Busang destroys many of the sample records.
1997: After many major miners express interest in Bre-X, eventually a joint venture is reached that gives Indonesia 40% share, Bre-X 45%, and Freeport McMoRan a 15% share of interests.
1997: Freeport begins due diligence on deposit and starts to twin holes that were already drilled.
1997: Freeport reports “minor amounts of gold” in some holes, but not much else.
1997: On his way to meet the Freeport due diligence team, de Guzman mysteriously falls to his death 600 ft from a helicopter. Police rule it a suicide.
1997: Shares of Bre-X crash.
1997: Report confirms that there is no gold at Busang, and samples were tampered with.
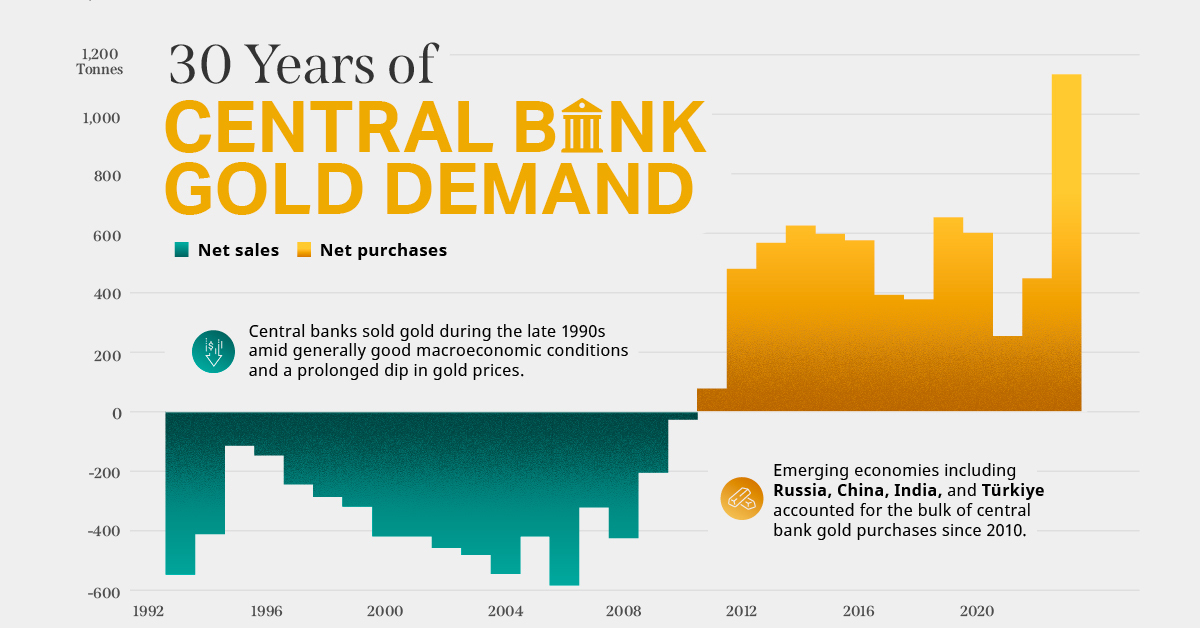
on Did you know that nearly one-fifth of all the gold ever mined is held by central banks? Besides investors and jewelry consumers, central banks are a major source of gold demand. In fact, in 2022, central banks snapped up gold at the fastest pace since 1967. However, the record gold purchases of 2022 are in stark contrast to the 1990s and early 2000s, when central banks were net sellers of gold. The above infographic uses data from the World Gold Council to show 30 years of central bank gold demand, highlighting how official attitudes toward gold have changed in the last 30 years.
Why Do Central Banks Buy Gold?
Gold plays an important role in the financial reserves of numerous nations. Here are three of the reasons why central banks hold gold:
Balancing foreign exchange reserves Central banks have long held gold as part of their reserves to manage risk from currency holdings and to promote stability during economic turmoil. Hedging against fiat currencies Gold offers a hedge against the eroding purchasing power of currencies (mainly the U.S. dollar) due to inflation. Diversifying portfolios Gold has an inverse correlation with the U.S. dollar. When the dollar falls in value, gold prices tend to rise, protecting central banks from volatility. The Switch from Selling to Buying In the 1990s and early 2000s, central banks were net sellers of gold. There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment. Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis. Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021: Rank CountryAmount of Gold Bought (tonnes)% of All Buying #1🇷🇺 Russia 1,88828% #2🇨🇳 China 1,55223% #3🇹🇷 Türkiye 5418% #4🇮🇳 India 3956% #5🇰🇿 Kazakhstan 3455% #6🇺🇿 Uzbekistan 3115% #7🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia 1803% #8🇹🇭 Thailand 1682% #9🇵🇱 Poland1282% #10🇲🇽 Mexico 1152% Total5,62384% Source: IMF The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period. Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar. Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework. Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022? In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Country2022 Gold Purchases (tonnes)% of Total 🇹🇷 Türkiye14813% 🇨🇳 China 625% 🇪🇬 Egypt 474% 🇶🇦 Qatar333% 🇮🇶 Iraq 343% 🇮🇳 India 333% 🇦🇪 UAE 252% 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan 61% 🇹🇯 Tajikistan 40.4% 🇪🇨 Ecuador 30.3% 🌍 Unreported 74165% Total1,136100% Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions. Share via: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn More
There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment.
Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis.
Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021:
Source: IMF
The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period.
Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar.
Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework.
Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022?
In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.