Is India the Next China? [Chart]
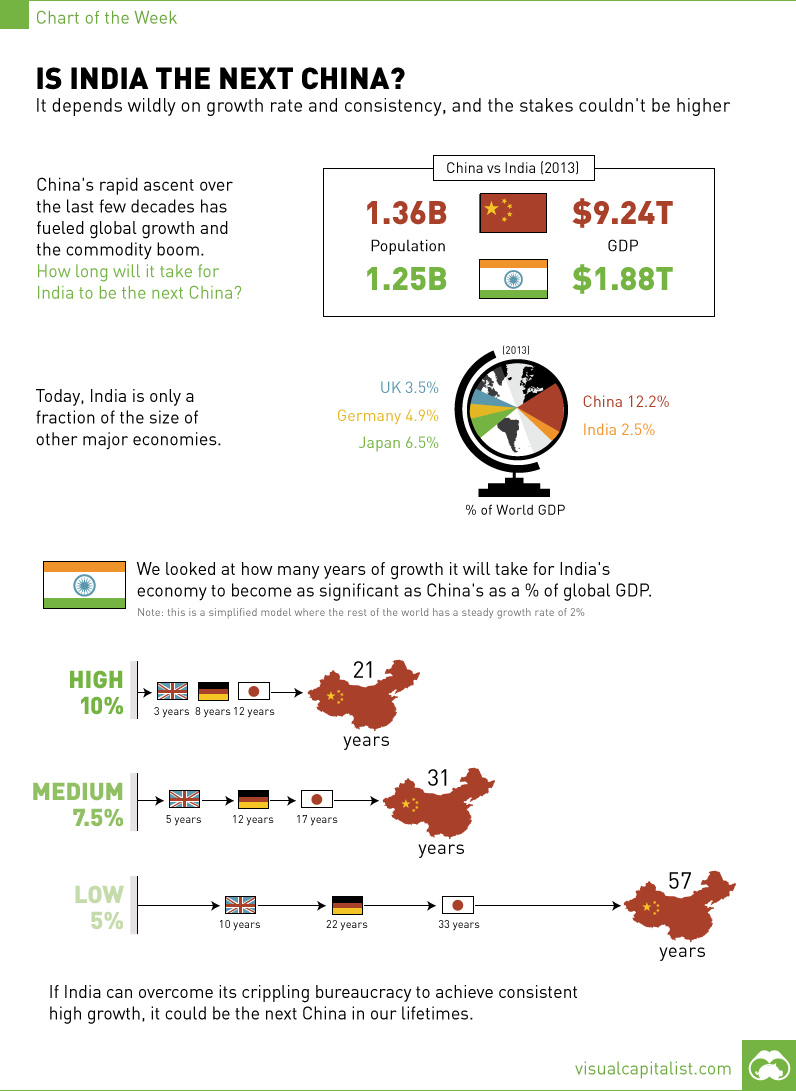
The Chart of the Week is a weekly feature in Visual Capitalist on Fridays. It’s no secret that the most recent bull market in commodities and global growth corresponded with the emergence of China on the world stage. When a country with over 1 billion people can grow at 10% for decades at a time, the power of compound interest starts to add up. The only problem is that Chinese growth is starting to slow down. To start 2015, the world’s second-biggest economy grew at its slowest pace in six years at a clip of 7.0%, which was down from 7.3% in Q4 2014. Further, the rate of growth in investment, industrial production, and retail sales have been declining consistently over the last four years. The world is looking for a new China to be the world’s growth engine. Does India fit the bill? No one is denying that India has the potential to be a game-changer for the global economy. With 1.25 billion people and growing, India will be the most populous country in the world by 2028. The challenge is that the majority of people in the country are terribly poor (GDP per capita of US$1,500) and that the country’s bureaucracy strangles almost and all business endeavours. That said, there are recent economic and bureaucracy reform green shoots that show that India could at least temporarily swing out of its funk. We did some back of the envelope calculations to see at what rate India would have to grow to be as significant to the world economy as China is today. We looked at India growing at high (10%), medium (7.5%), and low (5%) rates over the coming years. Based on this, India wouldn’t be comparable to today’s China until 21 years, 31 years, or 57 years respectively. (Note: to keep model simple, we had the rest of the world growing at a steady pace of 2%) The end result shows the staggering power of compound interest: if India grows at a high rate similar to China over the last decades, India could be a world player in the coming decades. If growth is crippled by bureaucracy and it hovers around 5% on average, India won’t become the next China until way in our future: the year 2072. On the bright side, Brazil may also be a good “bridge” for global growth. China certainly believes so, and that’s why they just announced an investment of $50 billion into the country’s infrastructure projects.
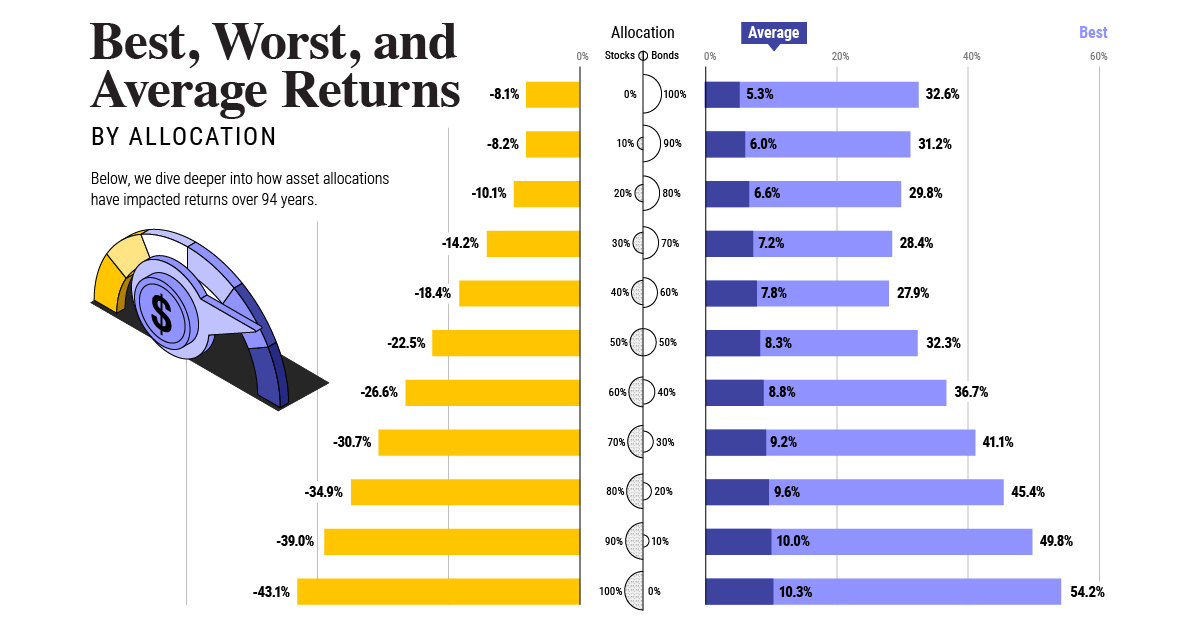
on Last year, stock and bond returns tumbled after the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates at the fastest speed in 40 years. It was the first time in decades that both asset classes posted negative annual investment returns in tandem. Over four decades, this has happened 2.4% of the time across any 12-month rolling period. To look at how various stock and bond asset allocations have performed over history—and their broader correlations—the above graphic charts their best, worst, and average returns, using data from Vanguard.
How Has Asset Allocation Impacted Returns?
Based on data between 1926 and 2019, the table below looks at the spectrum of market returns of different asset allocations:
We can see that a portfolio made entirely of stocks returned 10.3% on average, the highest across all asset allocations. Of course, this came with wider return variance, hitting an annual low of -43% and a high of 54%.
A traditional 60/40 portfolio—which has lost its luster in recent years as low interest rates have led to lower bond returns—saw an average historical return of 8.8%. As interest rates have climbed in recent years, this may widen its appeal once again as bond returns may rise.
Meanwhile, a 100% bond portfolio averaged 5.3% in annual returns over the period. Bonds typically serve as a hedge against portfolio losses thanks to their typically negative historical correlation to stocks.
A Closer Look at Historical Correlations
To understand how 2022 was an outlier in terms of asset correlations we can look at the graphic below:
The last time stocks and bonds moved together in a negative direction was in 1969. At the time, inflation was accelerating and the Fed was hiking interest rates to cool rising costs. In fact, historically, when inflation surges, stocks and bonds have often moved in similar directions. Underscoring this divergence is real interest rate volatility. When real interest rates are a driving force in the market, as we have seen in the last year, it hurts both stock and bond returns. This is because higher interest rates can reduce the future cash flows of these investments. Adding another layer is the level of risk appetite among investors. When the economic outlook is uncertain and interest rate volatility is high, investors are more likely to take risk off their portfolios and demand higher returns for taking on higher risk. This can push down equity and bond prices. On the other hand, if the economic outlook is positive, investors may be willing to take on more risk, in turn potentially boosting equity prices.
Current Investment Returns in Context
Today, financial markets are seeing sharp swings as the ripple effects of higher interest rates are sinking in. For investors, historical data provides insight on long-term asset allocation trends. Over the last century, cycles of high interest rates have come and gone. Both equity and bond investment returns have been resilient for investors who stay the course.